Date Functions
Date functions allow you to perform various tasks with dates. For example, to get the current date and time, format the display of a date, or retrieve specific parts of a date.
Notes:
-
The parameter required for date functions can be one of:
-
Literal date - #01/02/2025#
-
String date - "03/04/2025 12:57:20"
-
Input data field with either a date or a string that can be parsed as a date
-
Variable with either a date or a string that can be parsed as a date
-
A QLingo expression that results in either a date or a string that can be parsed as a date
-
-
Literal dates only must be formatted as #dd/mm/yyyy# or #dd/mm/yy# and must use a leading zero when necessary for single digits. For example: July 4, 2010 would be entered as #04/07/2010#
-
String dates must use a delimiter between month, day and year. The following delimiters are supported: / (forward slash), \ (back slash), – (dash) and . (period).
-
The format of the date from the data is locale specific; meaning it will use the regional date setup on your computer to read dd/mm/yy or mm/dd/yy. The examples shown on this page are in the format dd/mm/yy.
Date functions in QLingo include:
Note: Click here to download a sample file containing a data set, plan and InDesign template using the example values and functions on this page.
The following table shows values used in the numeric function examples below. You can also download the full sample file for additional context.
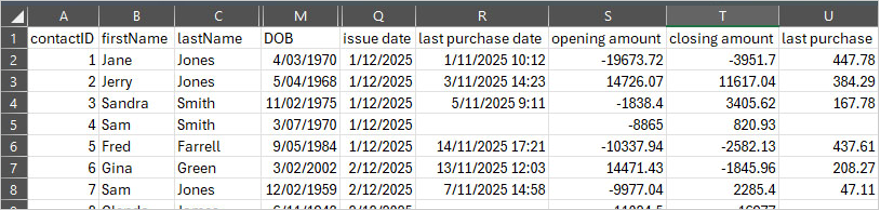
GetDay function
The GetDay function gets the day (1 to 31) of the date expression.
Syntax
GetDay(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The number returned represents the day part of the date entered as a parameter.
Examples
-
Get the day from a date literal.
GetDay(#01/02/2025#)
Result: 1
-
Get the day from a string.
GetDay("02/07/2006 12:57:20")
Result: 2
-
Get the day of a recipient's date of birth [DOB] input data field.
GetDay(|->[DOB])Recipient #1
Field: [DOB]: "4/03/1970"
Result: 4
-
Add 30 days to the [issue date] and then get the day.
GetDay(AsDate(|->[issue date]) + 30)Recipient #1
Field: [issue date] = "1/12/2025"
Calculation:
AsDate("1/12/2025") = #01/12/2025#
#01/12/2025# + 30 = #31/12/2025#
GetDay(#31/12/2025#) = 31Result: 31
Recipient #6
Field: [issue date] = "2/12/2025"
Calculation:
AsDate("2/12/2025") = #02/12/2025#
#02/12/2025# + 30 = #01/01/2026#
GetDay(#01/01/2026#) = 1Result: 1
GetMonth function
The GetMonth function gets the month (1 to 12) of the date expression.
Syntax
GetMonth(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The number returned represents the month part of the date entered as a parameter.
Examples
-
Get the month from a date literal.
GetMonth(#01/02/2025#)
Reult: 2
-
Get the month from a string.
GetMonth("02/07/2006 12:57:20")
Result: 7
-
Get the month of a recipient's date of birth [DOB] input data field.
GetMonth(|->[DOB])Recipient #1
Field: [DOB] = "4/03/1970"
Result: 3
-
Add 30 days to the [issue date] and then get the month.
GetMonth(AsDate(|->[issue date]) + 30)Recipient #1
Field: [issue date]: "1/12/2025"
Calculation:
AsDate("1/12/2025") = #01/12/2025#
#01/12/2025# + 30 = #31/12/2025#
GetMonth(#31/12/2025#) = 12Result: 12
Recipient #6
Field: [issue date] = "2/12/2025"
Calculation:
AsDate("2/12/2025") = #02/12/2025#
#02/12/2025# + 30 = #01/01/2026#
GetMonth(#01/01/2026#) = 1Result: 1
GetYear function
The GetYear function gets the year of the date expression.
Syntax
GetYear(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The number returned represents the year part of the date entered as a parameter.
Examples
-
Get the year from a date literal.
GetYear(#01/02/2025#)
Result: 2025
-
Get the year from a string.
GetYear("02/07/2006 12:57:20")
Result: 2006
-
Get the year of a recipient's date of birth [DOB] input data field.
GetYear(|->[DOB])Recipient #1
Field: [DOB] = "4/03/1970"
Result: 1970
-
Add 30 days to the [issue date] and then get the year.
GetYear(AsDate(|->[issue date]) + 30)Recipient #1
Field: [issue date] = "1/12/2025"
Calculation:
AsDate("1/12/2025") = #01/12/2025#
#01/12/2025# + 30 = #31/12/2025#
GetYear(#31/12/2025#) = 2025Result: 2025
Recipient #6
Field: [issue date] = "1/12/2025"
Calculation:
AsDate("2/12/2025") = #02/12/2025#
#02/12/2025# + 30 = #01/01/2026#
GetYear(#01/01/2026#) = 2026Result: 2026
GetDayOfWeek function
The GetDayOfWeek function gets the day of the week (1 to 7, where 1 denotes Sunday) of the date expression.
Syntax
GetDayOfWeek(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The number returned represents the day of the week (1-7 where 1 = Sunday) of the date entered as a parameter.
Examples
-
Get the day of week from a date literal.
GetDayOfWeek(#01/02/2025#)
Result: 7
-
Get the day of week on which the recipient was born.
GetDayOfWeek(|->[DOB])Recipient #1
Field: [DOB] = "4/03/1970"
Result: 4
-
Get the day of week on which the recipient was born and then convert it to the day name.
Copyswitch(GetDayOfWeek(|->[DOB])
{
case 1: "Sunday"
case 2: "Monday"
case 3: "Tuesday"
case 4: "Wednesday"
case 5: "Thursday"
case 6: "Friday"
default: "Saturday"
}Recipient #1
Field: [DOB] = "4/03/1970"
Result: "Wednesday"Recipient #2
Field: [DOB] = "5/04/68"
Result: "Friday"
GetHour function
The GetHour function gets the hour (0 to 23) of the date expression.
Note that if the date expression contains only the date component and no time, then midnight (00:00:00) will be inferred.
Syntax
GetHour(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The number returned represents the hour part of the date entered as a parameter.
Examples
-
Get the hour from a date literal where no time is provided.
GetHour(#01/02/2025#)
Result: 0
-
Get the hour from a string.
GetHour("02/07/2006 12:57:20")
Result: 12
-
Get the hour of a recipient's [last purchase date] input data field.
GetHour(|->[last purchase date])Recipient #1
Field: [last purchase date] = "1/11/2025 10:12:58"
Result: 10Recipient #2
Field: [last purchase date] = "3/11/2025 14:23:51"
Result: 14
GetMinute function
The GetMinute function gets the minute (0 to 59) of the date expression.
Syntax
GetMinute(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The number returned represents the minute part of the date entered as a parameter.
Examples
-
Get the minute from a date literal where no time is provided.
GetMinute(#01/02/2025#)
Result: 0
-
Get the minute from a string.
GetMinute("02/07/2006 12:57:20")
Result: 57
-
Get the minute of a recipient's [last purchase date] input data field.
GetMinute(|->[last purchase date])Recipient #1
Field: [last purchase date] = "1/11/2025 10:12:58"
Result: 12Recipient #2
Field: [last purchase date] = "3/11/2025 14:23:51"
Result: 23
GetSecond function
The GetSecond function gets the second (0 to 59) of the date expression.
Syntax
GetSecond(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The number returned represents the second part of the date entered as a parameter.
Examples
-
Get the second from a date literal where no time is provided.
GetSecond(#01/02/2025#)
Result: 0
-
Get the second from a string.
GetSecond("02/07/2006 12:57:20")
Result: 20
-
Get the second of a recipient's [last purchase date] input data field.
GetSecond(|->[last purchase date])Recipient #1
Field: [last purchase date] = "1/11/2025 10:12:58"
Result: 58Recipient #2
Field: [last purchase date] = "3/11/2025 14:23:51"
Result: 51
Age function
The Age function calculates the number of years between the input date expression and the current date/time. The result is returned as a decimal.
Note: The Age function can be used for any date field, not just birth dates. For example, you can calculate time since a purchase, subscription start, or event.
Syntax
Age(date expression)
This function returns a number data type. The value represents the difference in years (as a decimal) between the input date and the current date/time.
Note: The result includes fractional years to represent partial time periods.
Examples
-
Get the number of years since a static date string.
Age ("31/01/1973")
Result (as of 25/11/2025): 52.8164383561644
-
Get the number of years since the recipient's date of birth [DOB] field.
Age (|->[DOB])Recipient #1
Field: [DOB]: "4/03/1970"
Result (as of 25/11/2025): 55.7287671232877Recipient #2
Field: [DOB]: "5/04/1968"
Result (as of 25/11/2025): 57.641095890411
-
Get the number of years since the recipient's date of birth [DOB] field and lower to the nearest full year.
Floor(Age (|->[DOB]))Recipient #1
Field: [DOB]: "4/03/1970"
Calculation (as of 25/11/2025):
Age("4/03/1970") = 55.7287671232877
Floor(55.7287671232877) = 55Result: 55
Recipient #2
Field: [DOB] = "5/04/1968"
Calculation (as of 25/11/2025):
Age("5/04/1968") = 57.641095890411
Floor(57.641095890411) = 57Result: 57
-
Get the number of days since the recipient's last purchase date.
Age(|->[last purchase date]) * 365Recipient #1
Field: [last purchase date] = "1/11/2025 10:12:58"
Calculation (as of 25/11/2025):
Age("1/11/2025 10:12:58") = 0.065753424657534
0.065753424657534 * 365 = 24Result: 24
Recipient #2
Field: [last purchase date] = "3/11/2025 14:23:51"
Calculation (as of 25/11/2025):
Age("3/11/2025 14:23:51") = 0.06027397260274
0.06027397260274 * 365 = 22Result: 22
Now function
The Now function gets the current date/time of the computer running the function.
Syntax
Now()
No parameters are expected. The result will be a date data type.
Examples
-
Return the current date and time.
Now()= "25/11/2025 1:57:20 PM"
-
Return the current date only.
FormatDate(Now(),"dd/MM/yyyy")= "25/11/2025"
-
What will be the date in 30 days time?
FormatDate(Now() + 30 ,"dd/MM/yyyy")= "25/12/2025"
FormatDate function
The FormatDate function returns the date provided in expression1 according to the format specification in expression2.
Syntax
FormatDate(expression1, expression2)
This function returns a string data type.
Examples
-
Format a static literal date to show the full day name, a comma, full month, day as 2 digits, a comma and year as four digits.
FormatDate(#27/06/2006#, "dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy")
Result: "Tuesday, June 27, 2006"
-
Format the recipient's date of birth to show full day name, a comma, full month, day as 2 digits, a comma and year as four digits.
FormatDate(|->[DOB], "dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy")Recipient #1
Field: [DOB] = "4/03/1970"
Result: "Wednesday, March 04, 1970"Recipient #2
Field: [DOB] = "5/04/1968"
Result: "Friday, April 05, 1968"
-
Add 30 days to the recipient's last purchase date and format the result to show short day name, short month, and day without leading zero on single digit days.
FormatDate(|->[last purchase date] + 30, "ddd MMM d")Recipient #1
Field: [last purchase date] = "1/11/2025 10:12:58"
Calculation:
AsDate("1/11/2025 10:12:58") = #01/11/2025 10:12:58#
#01/11/2025 10:12:58# + 30 = #01/12/2025 10:12:58#
FormatDate(#01/12/2025 10:12:58#, "ddd MMM d") = Mon Dec 1Result: Mon Dec 1
Recipient #2
Field: [last purchase date] = "3/11/2025 14:23:51"
Calculation:
AsDate("3/11/2025 14:23:51") = #03/11/2025 14:23:51#
#03/11/2025 14:23:51# + 30 = #03/12/2025 14:23:51#
FormatDate(#03/12/2025 14:23:51#, "ddd MMM d") = Wed Dec 3Result: Wed Dec 3
The following table shows the characters that can be used to format the date and the resulting date format:
|
Option |
Description |
|
d |
Displays the day as a number without a leading zero (for example, 1). |
|
dd |
Displays the day as a number with a leading zero (for example, 01). |
|
ddd |
Displays the day as an abbreviation (for example, Sun). |
|
dddd |
Displays the day as a full name (for example, Sunday). |
|
M |
Displays the month as a number without a leading zero (for example, January is represented as 1). |
|
MM |
Displays the month as a number with a leading zero (for example, 01/12/01). |
|
MMM |
Displays the month as an abbreviation (for example, Jan). |
|
MMMM |
Displays the month as a full month name (for example, January). |
|
y |
Displays the year number (0-9) without leading zeros. |
|
yy |
Displays the year in two-digit numeric format with a leading zero, if applicable. |
|
yyy |
Displays the year in three-digit numeric format. |
|
yyyy |
Displays the year in four-digit numeric format. |
|
h |
Displays the hour as a number without leading zeros using the 12-hour clock (for example, 1:15:15 PM). |
|
hh |
Displays the hour as a number with leading zeros using the 12-hour clock (for example, 01:15:15 PM). |
|
H |
Displays the hour as a number without leading zeros using the 24-hour clock (for example, 1:15:15). |
|
HH |
Displays the hour as a number with leading zeros using the 24-hour clock (for example, 01:15:15). |
|
m |
Displays the minute as a number without leading zeros (for example, 12:1:15). |
|
mm |
Displays the minute as a number with leading zeros (for example, 12:01:15). |
|
s |
Displays the second as a number without leading zeros (for example, 12:15:5). |
|
ss |
Displays the second as a number with leading zeros (for example, 12:15:05). |
|
T |
Displays an uppercase 'A' for any hour before noon; displays an uppercase 'P' for any hour between noon and 11:59 P.M. |
|
TT |
Displays an uppercase 'AM' for any hour before noon; displays an uppercase 'PM' for any hour between noon and 11:59 P.M. |
|
t |
Displays a lowercase 'a' for any hour before noon; displays an lowercase 'p' for any hour between noon and 11:59 P.M. |
|
tt |
Displays an lowercase 'am' for any hour before noon; displays an lowercase 'pm' for any hour between noon and 11:59 P.M. |
|
Any other |
Displays as is. |
